近日,太阳成集团陈江照研究员团队和河北工业大学陈聪副教授团队合作在国际知名学术期刊Chemical Engineering Journal(TOP期刊)上发表题为《Grain boundary defect passivation by in situ formed wide-bandgap lead sulfate for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells》的文章。在钙钛矿薄膜表面和晶界陷阱态辅助的非辐射复合阻碍了钙钛矿太阳能电池功率转换效率和稳定性的进一步提升。此外,钙钛矿薄膜差的湿度稳定性制约着钙钛矿太阳能电池的商业化应用。在本研究工作中,我们报道了一种多功能晶界修饰策略,即通过硫酸甲铵和碘化铅的化学反应在钙钛矿薄膜晶界处原位生成一层超薄宽带隙疏水硫酸铅(PbSO4)。通过该策略的构建,同时实现结晶调控、缺陷钝化及湿度稳定性增加。结果,基于PbSO4改性的器件实现了21.90%的效率,该效率远远高于对照器件的19.53%。而且,未封装改性的器件在80±5%的相对湿度老化250小时后仍然保持初始效率的71%。本工作提出了一种原位晶界修饰策略来同时提升器件的效率和稳定性,为钙钛矿太阳能电池商业化应用奠定了坚实的基础。
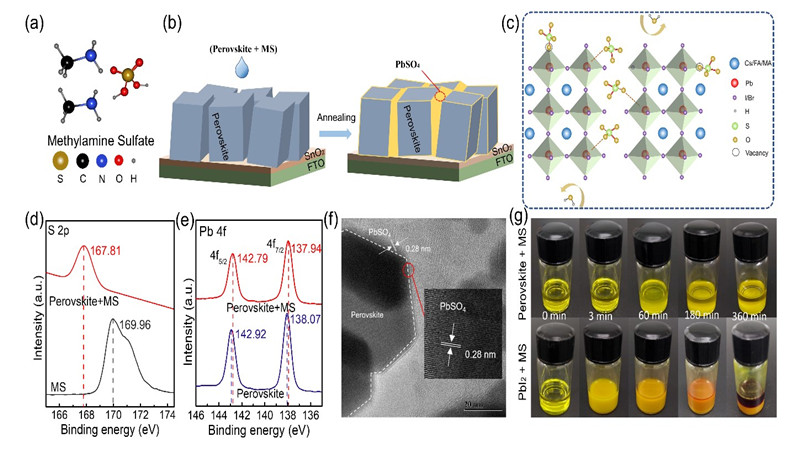
Fig. 1. (a) The chemical structure of MS. (b) Grain boundary in situ passivation strategy regulates humidity stability of perovskite light-absorbing layer by MS additive. (c) Schematic representation of possible in situ defect passivation mechanism and water repulsion induced by MS additive. (d) The XPS spectra of S 2p for the MS modified perovskite film and MS. (e) The XPS spectra of Pb 4f for the control and MS modified perovskite films. (f) HR-TEM image of the MS modified perovskite by ultrasonic dispersion treated the perovskite film in chlorobenzene. (g) After adding MS to the perovskite and PbI2 precursors, the changing phenomenon of solution over time.
文献链接:Xiaohui Ma, Liqun Yang, Xueni Shang, Mengjia Li, Deyu Gao, Cuncun Wu, Shijian Zheng*, Boxue Zhang, Jiangzhao Chen*, Cong Chen*, Hongwei Song*. Grain boundary defect passivation by in situ formed wide-bandgap lead sulfate for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Chemical Engineering Journal 2021, 130685: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1385894721022713.
 suncitygroup太阳新城官网
suncitygroup太阳新城官网